Logical fallacies — these logical gaps that invalidate arguments — aren’t at all times simple to identify.
Whereas some come within the type of loud, obtrusive inconsistencies, others can simply fly underneath the radar, sneaking into on a regular basis conferences and conversations undetected.
Our information on logical fallacies will make it easier to construct higher arguments and establish logical missteps.
Leap to:
What’s a logical fallacy?
Logical fallacies are misleading or false arguments which will appear stronger than they really are on account of psychological persuasion, however are confirmed fallacious with reasoning and additional examination.
These errors in reasoning sometimes encompass an argument and a premise that doesn’t help the conclusion. There are two sorts of fallacies: formal and casual.
- Formal: Formal fallacies are arguments which have invalid construction, type, or context errors.
- Casual: Casual fallacies are arguments which have irrelevant or incorrect premises.
Having an understanding of fundamental logical fallacies might help you extra confidently parse the arguments and claims you take part in and witness every day — separating truth from sharply dressed fiction.
15 Frequent Logical Fallacies
1. The Straw Man Fallacy
This fallacy happens when your opponent over-simplifies or misrepresents your argument (i.e., organising a “straw man”) to make it simpler to assault or refute. As an alternative of totally addressing your precise argument, audio system counting on this fallacy current a superficially comparable — however finally not equal — model of your actual stance, serving to them create the phantasm of simply defeating you.
Instance:
John: I feel we should always rent somebody to revamp our web site.
Lola: You are saying we should always throw our cash away on exterior assets as an alternative of build up our in-house design staff? That is going to harm our firm in the long term.
2. The Bandwagon Fallacy
Simply because a big inhabitants of individuals consider a proposition is true, does not robotically make it true. Recognition alone isn’t sufficient to validate an argument, although it is usually used as a standalone justification of validity. Arguments on this fashion do not have in mind whether or not or not the inhabitants validating the argument is definitely certified to take action, or if opposite proof exists.
Whereas most of us count on to see bandwagon arguments in promoting (e.g., “three out of 4 folks suppose X model toothpaste cleans enamel finest”), this fallacy can simply sneak its approach into on a regular basis conferences and conversations.
Instance:
The vast majority of folks consider advertisers ought to spend more cash on billboards, so billboards are objectively the very best type of commercial.
3. The Enchantment to Authority Fallacy
Whereas appeals to authority are on no account at all times fallacious, they will shortly grow to be harmful if you rely too closely on the opinion of a single particular person — particularly if that particular person is trying to validate one thing exterior of their experience.
Getting an authority determine to again your proposition is usually a highly effective addition to an current argument, however it could possibly’t be the pillar your total argument rests on. Simply because somebody able of energy believes one thing to be true, does not make it true.
Instance:
Although our This autumn numbers are a lot decrease than typical, we should always push ahead utilizing the identical technique as a result of our CEO Barbara says that is the very best method.
4. The False Dilemma Fallacy
This frequent fallacy misleads by presenting complicated points when it comes to two inherently opposed sides. As an alternative of acknowledging that the majority (if not all) points may be considered on a spectrum of potentialities and stances, the false dilemma fallacy asserts that there are solely two mutually unique outcomes.
This fallacy is especially problematic as a result of it could possibly lend false credence to excessive stances, ignoring alternatives for compromise or possibilities to re-frame the problem in a brand new approach.
Instance:
We will both agree with Barbara’s plan, or simply let the venture fail. There is no such thing as a different choice.
5. The Hasty Generalization Fallacy
This fallacy happens when somebody attracts expansive conclusions primarily based on insufficient or inadequate proof. In different phrases, they soar to conclusions in regards to the validity of a proposition with some — however not sufficient — proof to again it up, and overlook potential counterarguments.
Instance:
Two members of my staff have grow to be extra engaged staff after taking public talking courses. That proves we should always have obligatory public talking courses for the entire firm to enhance worker engagement.
6. The Slothful Induction Fallacy
Slothful induction is the precise inverse of the hasty generalization fallacy above. This fallacy happens when ample logical proof strongly signifies a selected conclusion is true, however somebody fails to acknowledge it, as an alternative attributing the result to coincidence or one thing unrelated fully.
Instance:
Though each venture Brad has managed within the final two years has run approach not on time, I nonetheless suppose we are able to chalk it as much as unlucky circumstances, not his venture administration expertise.
7. The Correlation/Causation Fallacy
If two issues look like correlated, this does not essentially point out that a type of issues irrefutably precipitated the opposite factor. This may appear to be an apparent fallacy to identify, however it may be difficult to catch in apply — significantly if you actually wish to discover a correlation between two factors of knowledge to show your level.
Instance:
Our weblog views had been down in April. We additionally modified the colour of our weblog header in April. Which means that altering the colour of the weblog header led to fewer views in April.
8. The Anecdotal Proof Fallacy
Rather than logical proof, this fallacy substitutes examples from somebody’s private expertise. Arguments that rely closely on anecdotal proof are inclined to overlook the truth that one (presumably remoted) instance cannot stand alone as definitive proof of a better premise.
Instance:
One in every of our shoppers doubled their conversions after altering all their touchdown web page textual content to vivid crimson. Due to this fact, altering all textual content to crimson is a confirmed solution to double conversions.
9. The Texas Sharpshooter Fallacy
This fallacy will get its colourful title from an anecdote a couple of Texan who fires his gun at a barn wall, after which proceeds to color a goal across the closest cluster of bullet holes. He then factors on the bullet-riddled goal as proof of his knowledgeable marksmanship.
Audio system who depend on the Texas sharpshooter fallacy are inclined to cherry-pick knowledge clusters primarily based on a predetermined conclusion. As an alternative of letting a full spectrum of proof make them a logical conclusion, they discover patterns and correlations in help of their objectives, and ignore proof that contradicts them or suggests the clusters weren’t really statistically vital.
Instance:
Lisa offered her first startup to an influential tech firm, so she should be a profitable entrepreneur. (She ignores the truth that 4 of her startups have failed since then.)
10. The Center Floor Fallacy
This fallacy assumes {that a} compromise between two excessive conflicting factors is at all times true. Arguments of this fashion ignore the chance that one or each of the extremes might be fully true or false — rendering any type of compromise between the 2 invalid as effectively.
Instance:
Lola thinks the easiest way to enhance conversions is to revamp all the firm web site, however John is firmly in opposition to making any adjustments to the web site. Due to this fact, the very best method is to revamp some parts of the web site.
11. The Burden of Proof Fallacy
If an individual claims that X is true, it’s their accountability to supply proof in help of that assertion. It’s invalid to assert that X is true till another person can show that X isn’t true. Equally, it’s also invalid to assert that X is true as a result of it is inconceivable to show that X is fake.
In different phrases, simply because there isn’t any proof introduced in opposition to one thing, that does not robotically make that factor true.
Instance:
Barbara believes the advertising company’s workplace is haunted, since nobody has ever confirmed that it is not haunted.
12. The Private Incredulity Fallacy
When you’ve got problem understanding how or why one thing is true, that does not robotically imply the factor in query is fake. A private or collective lack of knowledge is not sufficient to render a declare invalid.
Instance:
I do not perceive how redesigning our web site resulted in additional conversions, so there should have been one other issue at play.
13. The “No True Scotsman” Fallacy
Usually used to guard assertions that depend on common generalizations (like “all Entrepreneurs love pie”) this fallacy inaccurately deflects counterexamples to a declare by altering the positioning or circumstances of the unique declare to exclude the counterexample.
In different phrases, as an alternative of acknowledging {that a} counterexample to their unique declare exists, the speaker amends the phrases of the declare. Within the instance under, when Barabara presents a sound counterexample to John’s declare, John adjustments the phrases of his declare to exclude Barbara’s counterexample.
Instance:
John: No marketer would ever put two call-to-actions on a single touchdown web page.
Barbara: Lola, a marketer, really discovered nice success placing two call-to-actions on a single touchdown web page for our final marketing campaign.
John: Properly, no true marketer would put two call-to-actions on a single touchdown web page, so Lola should not be a real marketer.
14. The Advert Hominem Fallacy
An advert hominem fallacy happens if you assault somebody personally relatively than utilizing logic to refute their argument. As an alternative they’ll assault bodily look, private traits, or different irrelevant traits to criticize the opposite’s perspective. These assaults will also be leveled at establishments or teams.
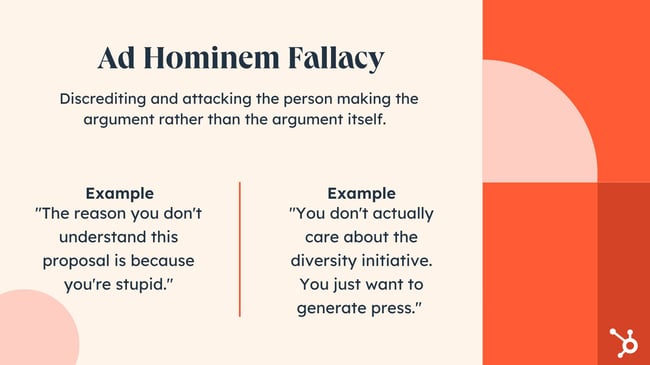
Instance:
Barbara: We must always evaluate these knowledge units once more simply to make sure they’re correct.
Tim: I figured you’ll recommend that because you’re a bit sluggish on the subject of math.
15. The Tu Quoque Fallacy
The tu quoque fallacy (Latin for “you additionally”) is an invalid try to discredit an opponent by answering criticism with criticism — however by no means really presenting a counterargument to the unique disputed declare.
Within the instance under, Lola makes a declare. As an alternative of presenting proof in opposition to Lola’s declare, John ranges a declare in opposition to Lola. This assault does not really assist John reach proving Lola fallacious, since he does not deal with her unique declare in any capability.
Instance:
Lola: I do not suppose John could be a superb match to handle this venture, as a result of he does not have loads of expertise with venture administration.
John: However you do not have loads of expertise in venture administration both!
16. The Fallacy Fallacy
Here is one thing important to remember when sniffing out fallacies: simply because somebody’s argument depends on a fallacy does not essentially imply that their declare is inherently unfaithful.
Making a fallacy-riddled declare does not robotically invalidate the premise of the argument — it simply means the argument does not really validate their premise. In different phrases, their argument sucks, however they don’t seem to be essentially fallacious.
Instance:
John’s argument in favor of redesigning the corporate web site clearly relied closely on cherry-picked statistics in help of his declare, so Lola determined that redesigning the web site should not be a superb determination.
Acknowledge Logical Fallacies
Recognizing logical fallacies once they happen and studying the best way to fight them will show helpful for navigating disputes in each private {and professional} settings. We hope the information above will make it easier to keep away from a number of the most typical argument pitfals and make the most of logic as an alternative.
This text was revealed in July 2018 and has been up to date for comprehensiveness.


